10 smart tips for getting vitamin D
/10 smart tips for getting vitamin D
Vitamin D can be a rather elusive vitamin for obtaining what we need for good health. It’s not abundantly found in many food sources and our main way of getting it is from the sun. This can make it difficult if you live in a northern state such as Minnesota or Maine, in which the sun rays are not strong enough from October through about March to enable our bodies to produce vitamin D.
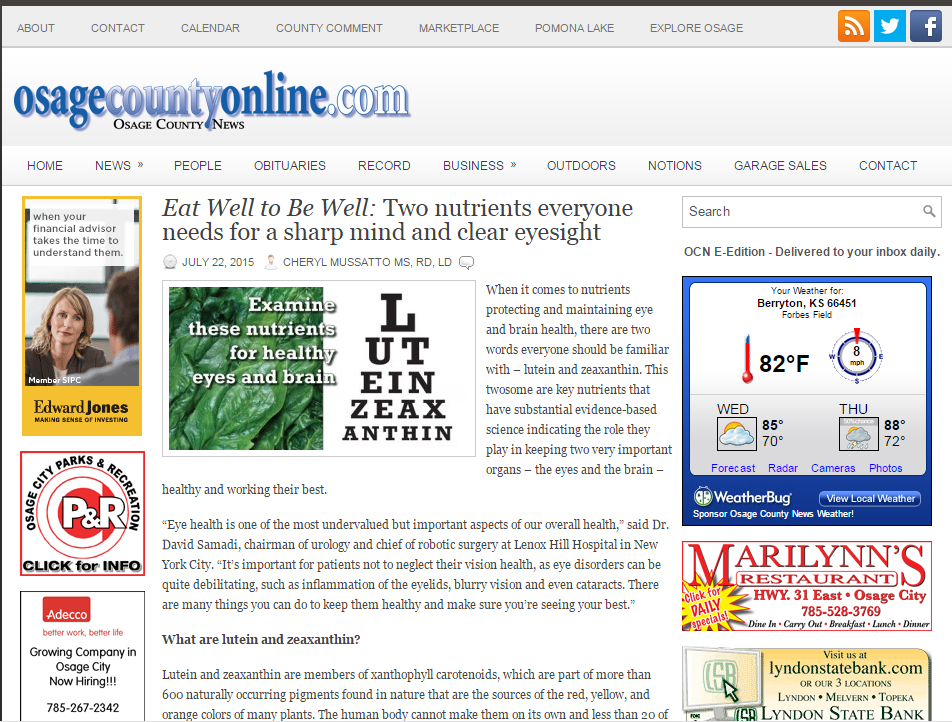
Vitamin D is essential for many important functions in our body. It is needed to maintain normal levels of the minerals calcium and phosphorus in the blood important for bone health. Vitamin plays a role in regulating blood levels of calcium so that a steady supply is available when and where it is needed. In addition, it is necessary for proper functioning of nerves, muscles, glands, and other tissues.
The Recommend Dietary Allowance (RDA) of daily vitamin D is:
· 600 International Units (IU) for children and adults under age 70
· 800 IU for adults older than 70
· 400 IU for infants
To avoid developing a vitamin D deficiency, here are 10 ways that are your best bet for ensuring an adequate intake:
1. Sufficient sunlight – There’s a reason vitamin D has the nickname “the sunshine vitamin.” Sunlight is our best source of helping us make vitamin D on our own. The best time of day to be out in the sunlight helping this process along is midday or at 12 noon, when our shadow is the shortest. If you can spend at least 15 -30 minutes or so in the sun with at least your hands, arms or face exposed about 3-4 times a week, this can do the trick for the production of vitamin D.
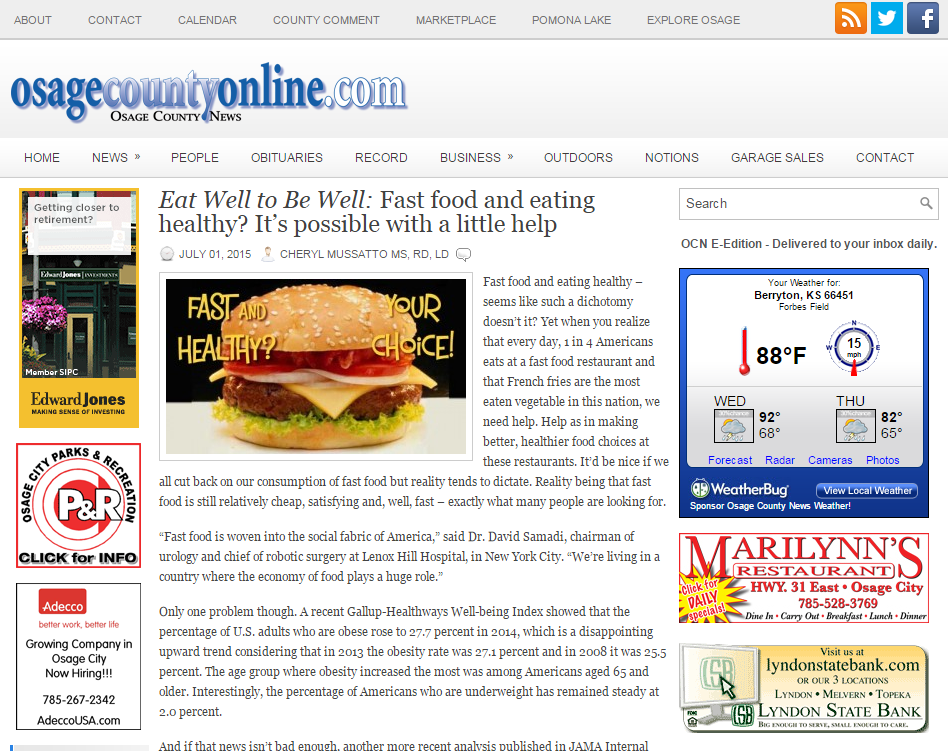
2. Eat fatty fish – One of the best food sources of vitamin D is fatty fish which include salmon, trout, mackerel, tuna, and sardines. A 3-ounce portion of salmon contains about 450 international units (IU) of vitamin D.
3. Eat canned fish – Canned fish such as tuna, salmon, or sardines are also good ways of boosting your vitamin D intake. Fresh fatty fish may be cost prohibitive for many people - the canned versions still contain vitamin D and are much less expensive.
Plus, canned fish have a much longer shelf life making it easy to stock up and use at your convenience. Canned light tuna has the most vitamin D – about 150 IU per 4 ounces, while canned albacore tuna has about 50 IU per 4 ounces.
3. Mushrooms – Like humans, mushrooms exposed to the ultraviolet rays from the sun, provides the capacity to produce vitamin D. However, mushrooms are usually grown in the dark and do not contain vitamin D. But certain types and brands of mushrooms are grown in ultraviolet light to stimulate vitamin production. Look for mushrooms at the grocery store where it indicates on the label if they are vitamin D-rich.
4. Milk fortified with vitamin D – Since the 1940s, cow’s milk has been fortified with vitamin D. Vitamin D does not naturally occur in cow’s milk but the reason why it was added to milk decades ago was to prevent rickets – the vitamin D deficiency disease in children. An 8-ounce glass of milk – skim, 1%, 2% and whole - usually contains at least 100 IUs of vitamin D.
5. Some orange juices – In the past several years, a new food has been boasting of its vitamin D content – orange juice. Like milk, orange juice does not naturally contain vitamin D and not all brands of orange juice are fortified with it, so check the label. Of the orange juice brands that do fortify their juice with vitamin D, an 8-ounce glass will provide about 100 IUs.
6. Supplements of vitamin D – A common way many people are relying upon to get adequate vitamin D stores are by taking a supplement of the nutrient. Too much vitamin D taken as a pill form however, can be toxic. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin meaning we can store this vitamin. The Institute of Medicine has set the upper intake level of a supplement of vitamin at 4,000 IUs per day for people aged 9 and older. However, for people who are vitamin D deficient as determined by a blood test, their healthcare provider may recommend a higher dosage for a recommend amount of time to take to boost intake. Food sources of vitamin and being in the sun cannot cause a toxic level of vitamin D.
7. Egg yolks – The yolk of eggs are a convenient way of providing vitamin D. Eggs are a popular food especially for breakfast with one yolk providing about 40 IUs. Since the vitamin D found in eggs comes only from the yolk, it is important to eat the whole egg – not just the whites.
8. Fortified breakfast cereal – Here is another breakfast food containing vitamin D added to it. Check the Nutrition Facts Label to see if the breakfast cereal of your choice has been fortified with vitamin D as not all are. The amount of vitamin D in a fortified cereal will vary depending on the brand.
9. Beef liver – Not everyone is crazy about eating liver but for those that are, beef liver is a good source. A 3.5 ounce serving of cooked beef liver contains 50 IUs of vitamin D along with vitamin A, iron, and protein.
10. Cod liver oil – Here’s an old standby often used decades ago to supply sufficient vitamin D. One tablespoon contains about 1,300 IUs of vitamin D which is more than twice the recommended dietary allowance of 600 IUs per day. If the thought of using cod liver oil as your go-to source for this vitamin sounds disgusting, it is available flavored with mint or citrus and also comes in capsule form.