Medications that can contribute to weight gain
/Medications that can contribute to weight gain
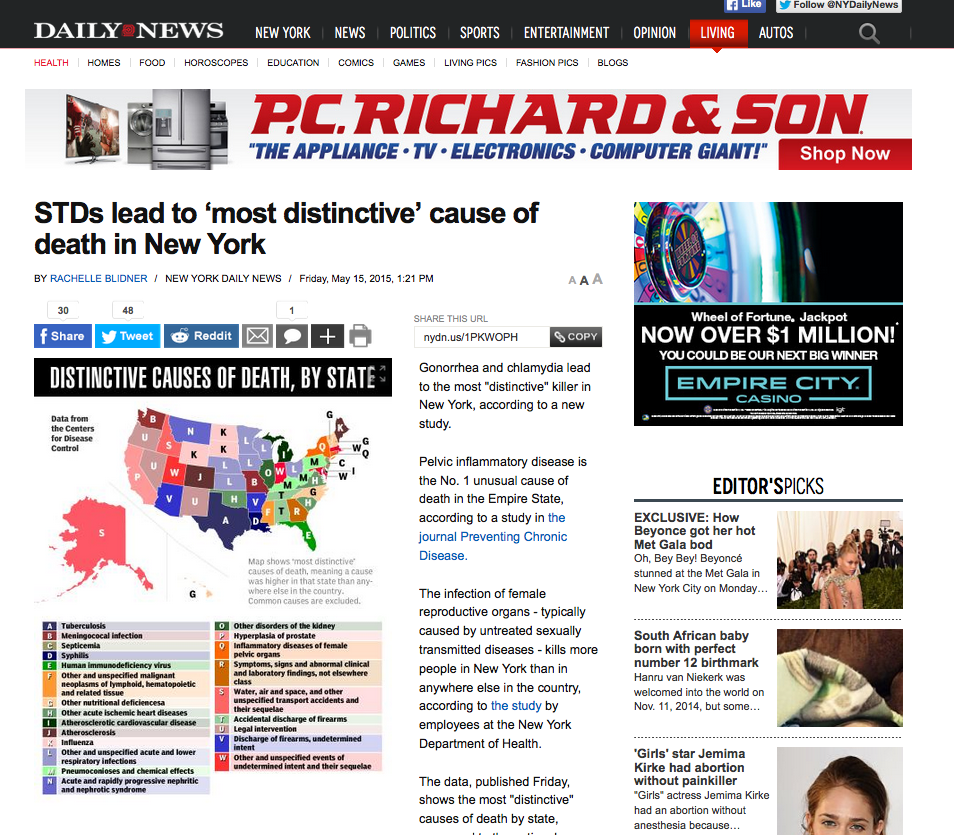
It’s a hard pill to swallow but your medications could be contributing to weight gain. You may be watching what you eat and fitting in regular workouts but the number on your scale continues to rise. If that is the case, what is a person to do? Conditions such as diabetes, depression, high blood pressure, seizures, some steroids, hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptives, and migraines all depend on people taking their prescribed medications. But when a person notices clothes getting tighter or the number on the scale rising, it can lead to feelings of frustration when all you want is to control your medical condition but without extra pounds gained.
First, if you suspect a prescribed drug is causing weight gain, never stop taking the medication on your own as it can have serious consequences – they usually need to be weaned off gradually under a doctor’s guidance.
Why do some medications cause weight gain?
There can be a variety of reasons why certain medications may cause weight gain. Here is a look at more common prescription medications that have a tendency to result in extra pounds:
· Steroids
The side effect of weight gain when using a steroid depends on the amount of steroid one is taking and the length of time using the drug. It is well known that many people may gain weight when on a steroid such as prednisone. The amount of weight gain will vary amongst people but one of the more annoying aspects of the weight gained is the redistribution of body fat to areas of the body – the face, back of the neck, and abdomen.
Steroids affect your metabolism and how your body deposits fat. In addition, they can affect your metabolism and how your body deposits fat and increase appetite leading to weight gain.
· Antidepressants
Nearly all antidepressants can cause weight gain but each individual will respond differently to this medication. Even though some people will gain weight after starting an antidepressant, the antidepressant isn’t always the direct cause for it.
Some reasons for weight gain while on an antidepressant include being inactive or overeating due to being depressed, older individuals who have a slowed metabolism, or regaining an appetite after using an antidepressant.
It helps to consult with your doctor if weight gain occurs after starting an antidepressant to look into the possibility of adjusting the dose or switching to another medication.
· Diabetes medication
Anyone with diabetes knows the importance of eating a healthy diet and to lose some weight but what if the diabetes medication is contributing to weight gain? Not all people with diabetes will experience weight gain from their meds but some do. Part of the reason could be those needing to inject insulin. A function of insulin is to help get glucose out of the bloodstream and into the body’s cells – in doing so it may cause weight gain. Another reason is when insulin is increased, it causes the body to retain more calories in addition to reducing the amount of glucose excreted in the urine causing the body to reabsorb the glucose and storing it as fat.
· Mood stabilizers
These drugs help treat mental health conditions such as bipolar disorder or schizophrenia. They work by directly affecting your brain and will affect your weight and metabolism. Mood stabilizers can cause your appetite to increase and stay that way. Some may cause as much as a 10-pound weight gain in 10 weeks. If you have to be on them long term, even more weight gain is likely.
· Drugs preventing seizures and migraines
Medicines that stop migraine headaches and seizures affect hormones that control hunger and make it harder for your body to sense when it is full. They increase appetite while lowering metabolism and can cause your body to hang on to extra fluids.
· Beta blocker heart medications
Beta blockers ease stress on your heart by slowing its rate and lowering blood pressure. But this also reduces the body’s reaction to exercise therefore, fewer calories are burned. Beta blockers also make you feel tired which can result in you lacking energy to workout which can also lead to weight gain.
· Allergy relievers
Over-the-counter allergy medications can block the action of histamine, a chemical your body makes that causes many of the symptoms of allergies. Blocking histamine with an antihistamine may lead to weight gain.
Takeaway message
Again, do not stop taking any prescribed medication without discussing your concerns with your doctor. It is perfectly fine to bring up your concerns of excess weight gain as your doctor can advise you on the best way to prevent that. Be willing to work with your doctor on devising a dietary and exercise plan helping you stay fit and healthy while still allowing you to take your necessary medications with as little of weight gain as possible.