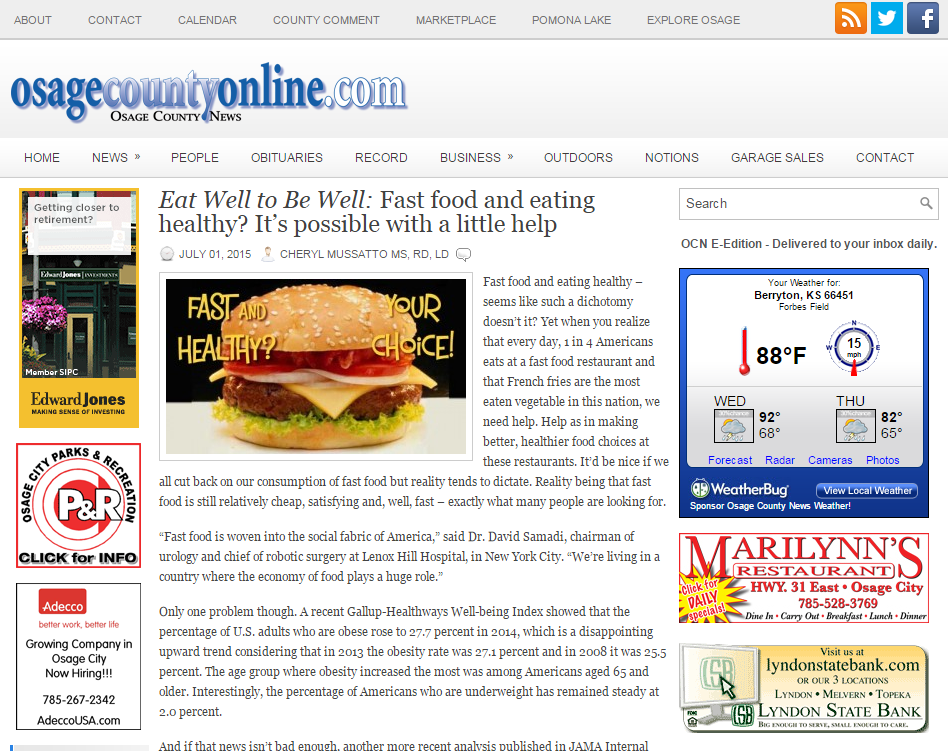
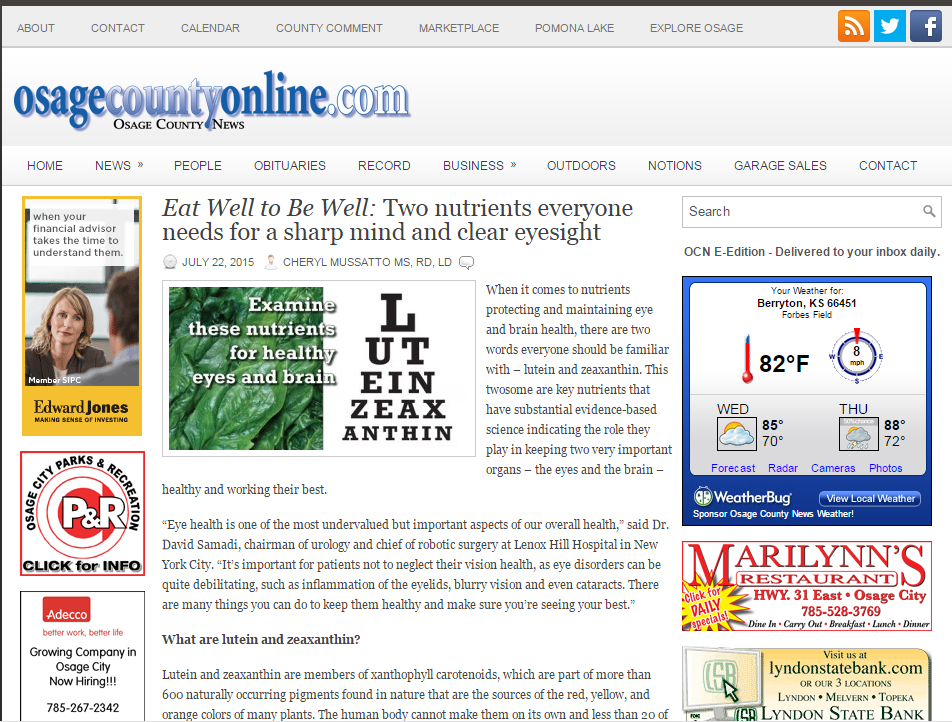
Sorting Out Diabetes
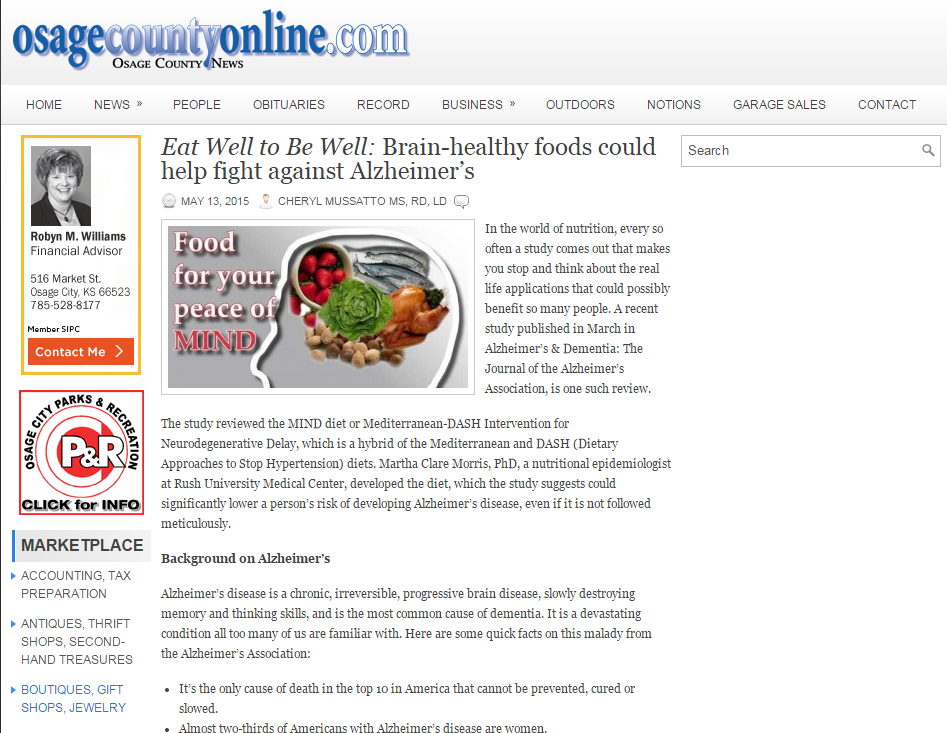
/Diabetes is when your body causes blood glucose (sugar) levels to rise higher than normal which is called hyperglycemia. Having diabetes means your body is either not making enough insulin or it can’t use the insulin it does make well, or both. Insulin is a hormone made by the beta cells in your pancreas, an organ which is behind the stomach.
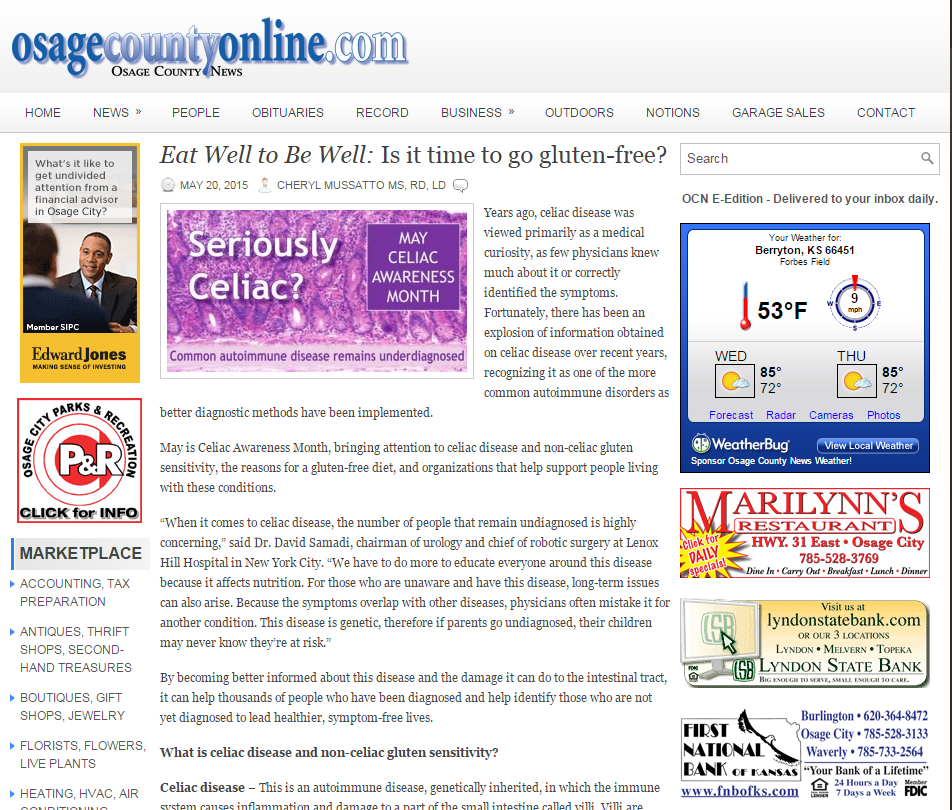
There are different types of diabetes – type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes which only occurs in women who are pregnant. Each type has symptoms that are similar but also vary from one another. Here is a look at symptoms a person may experience depending on which type of diabetes they have:
Type 1
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes are serious and usually occur quickly with the person feeling very sick due to high blood glucose levels. Common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
· Frequent urination as the body tries to flush out excess glucose in the blood
· Unusual thirst due to dehydration
· Unusual hunger due to the cells of the body being starved for energy
· Unusual tiredness due to the glucose not entering the cells giving them energy
· Blurred vision due to buildup of fluid in the lens of the eyes caused by high blood glucose levels
· Weight loss without trying due to the body not being able to use the food eaten
· Nausea and vomiting due to a buildup of ketones in the blood
Type 2
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can be the same or similar to type 1 diabetes but they tend to be vague and do not appear suddenly like they do in type 1 diabetes. A person may have no noticeable symptoms or only mild symptoms for years before it is diagnosed. Common symptoms of type 2 diabetes include:
· Urinating more frequently as the body tries to flush out excess glucose in the blood
· Unusual thirst due to dehydration
· Unusual hunger all the time because the cells of the body are starved for energy
· Unusual tiredness due to glucose not entering the cells of the body giving them energy
· Blurred vision because of buildup of fluid in the lens of the eyes caused by high blood glucose levels
· Frequent infections or slow healing of cuts and sores
· Tingling, pain, or numbness in the hands or feet
Gestational diabetes
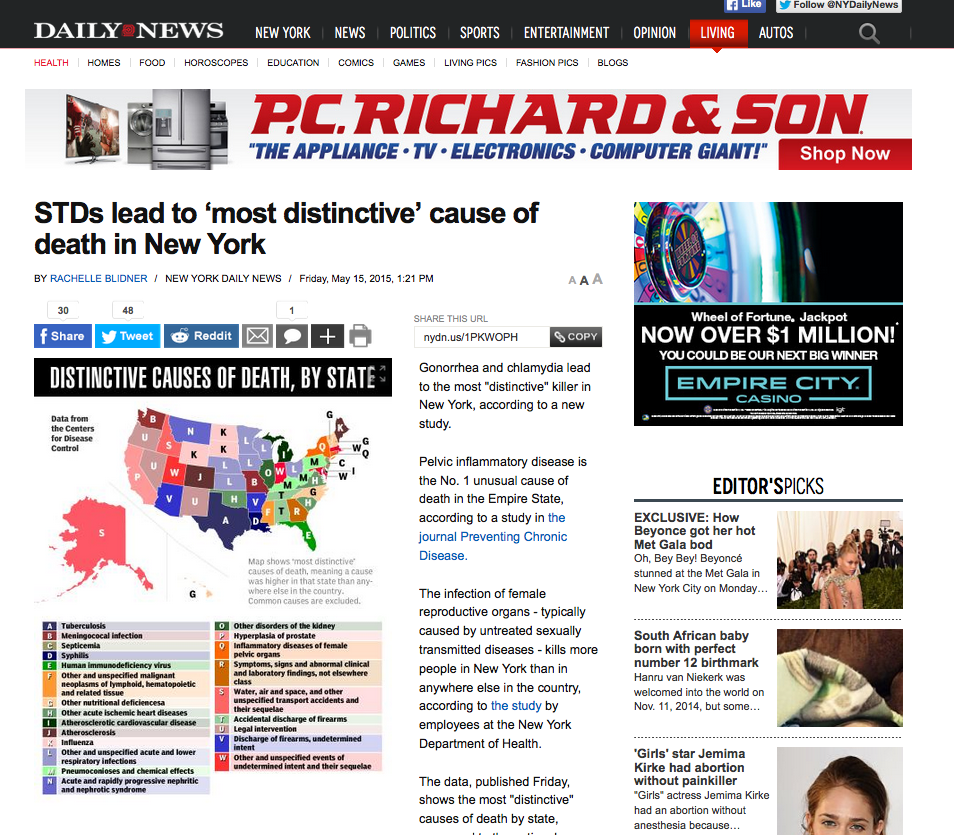
Gestational diabetes is when a woman develops high blood glucose levels during her pregnancy. It occurs in about 4 % of all pregnancies and is usually diagnosed in the later stages of the pregnancy. Gestational diabetes typically does not cause any noticeable signs or symptoms which is why all pregnant women need to be screened for it between the 24th and 28th week of pregnancy. Blood testing will confirm the diagnosis at which time the woman should be counseled by a registered dietitian on how to follow a healthy diet until the baby is born and how to prevent permanent diabetes from developing in the future.